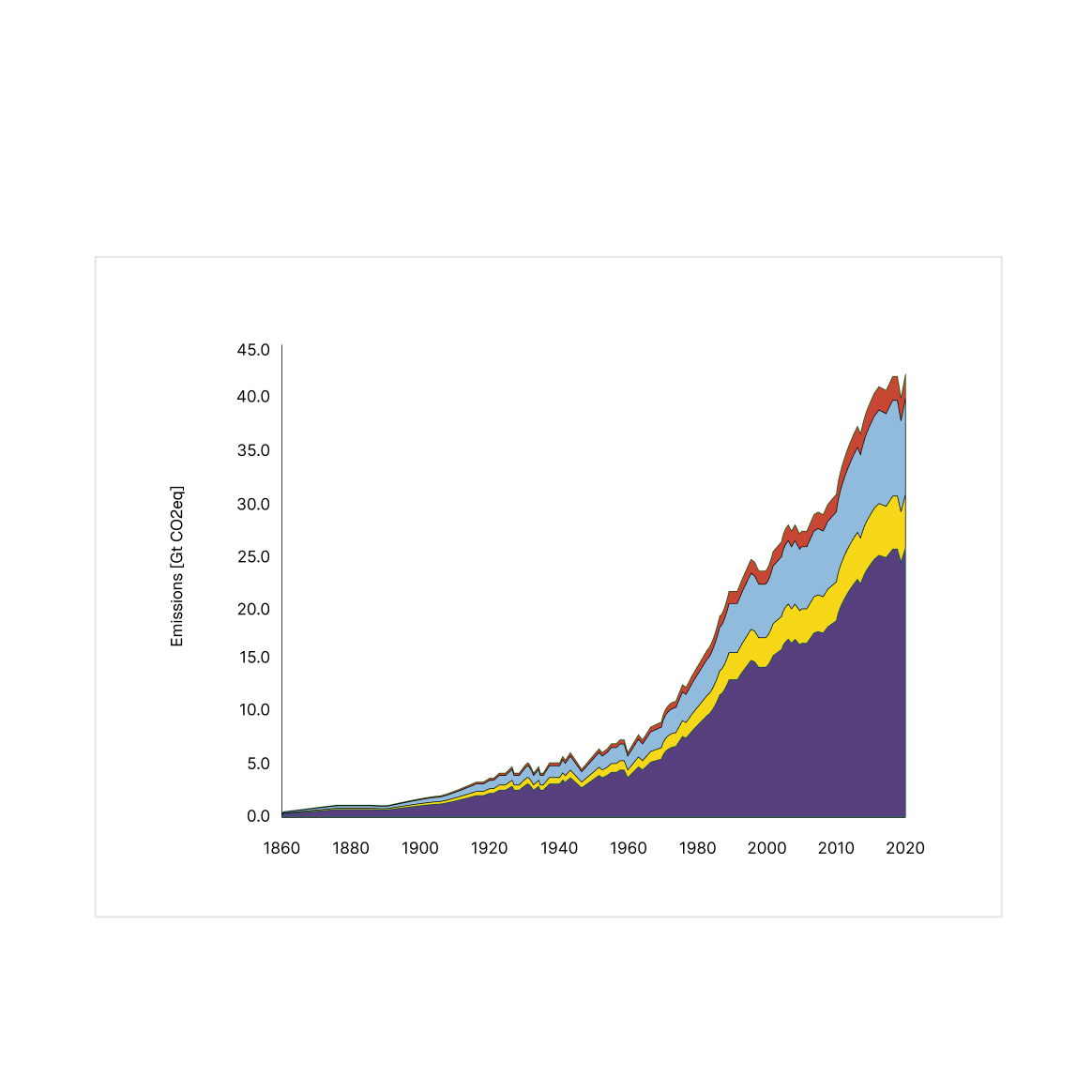
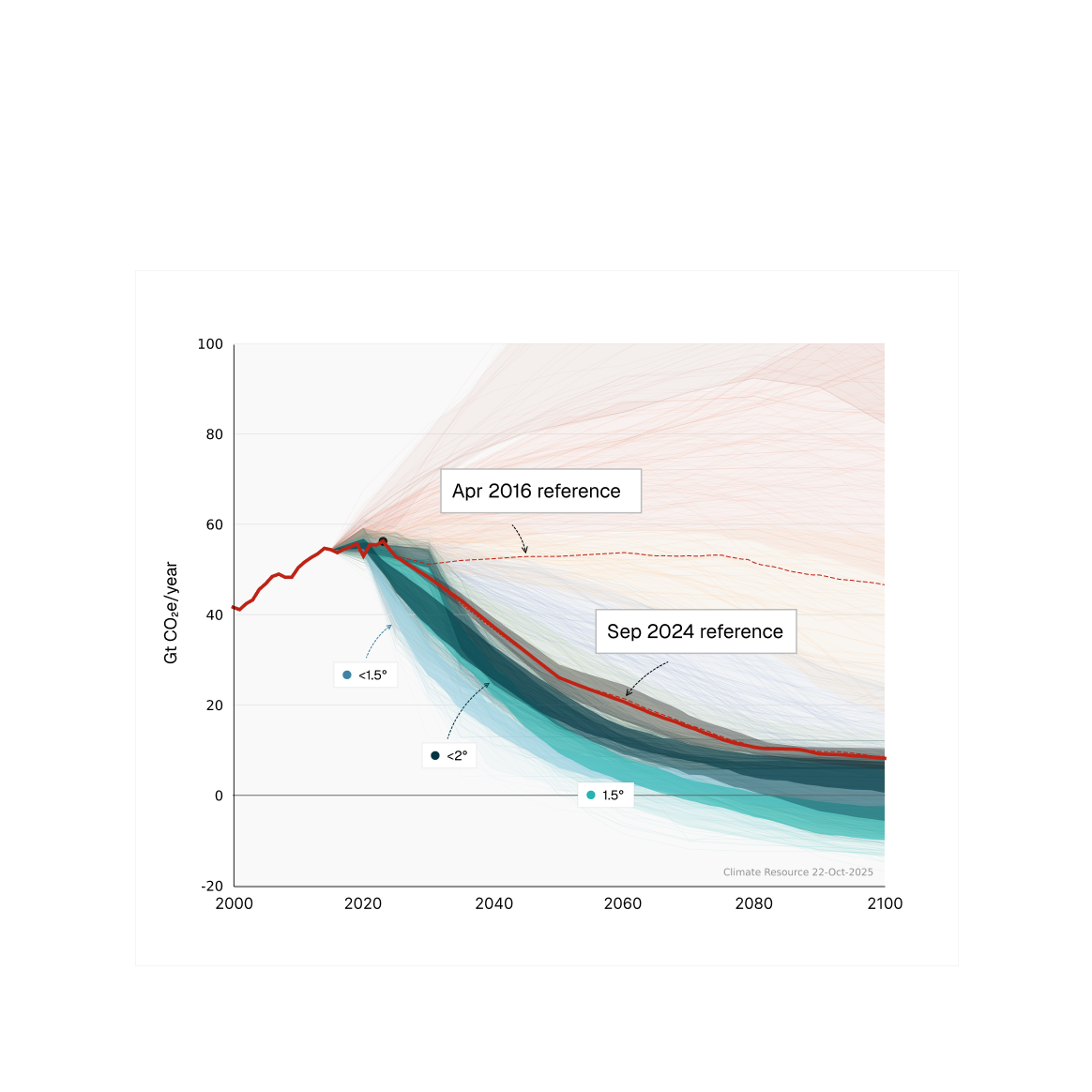
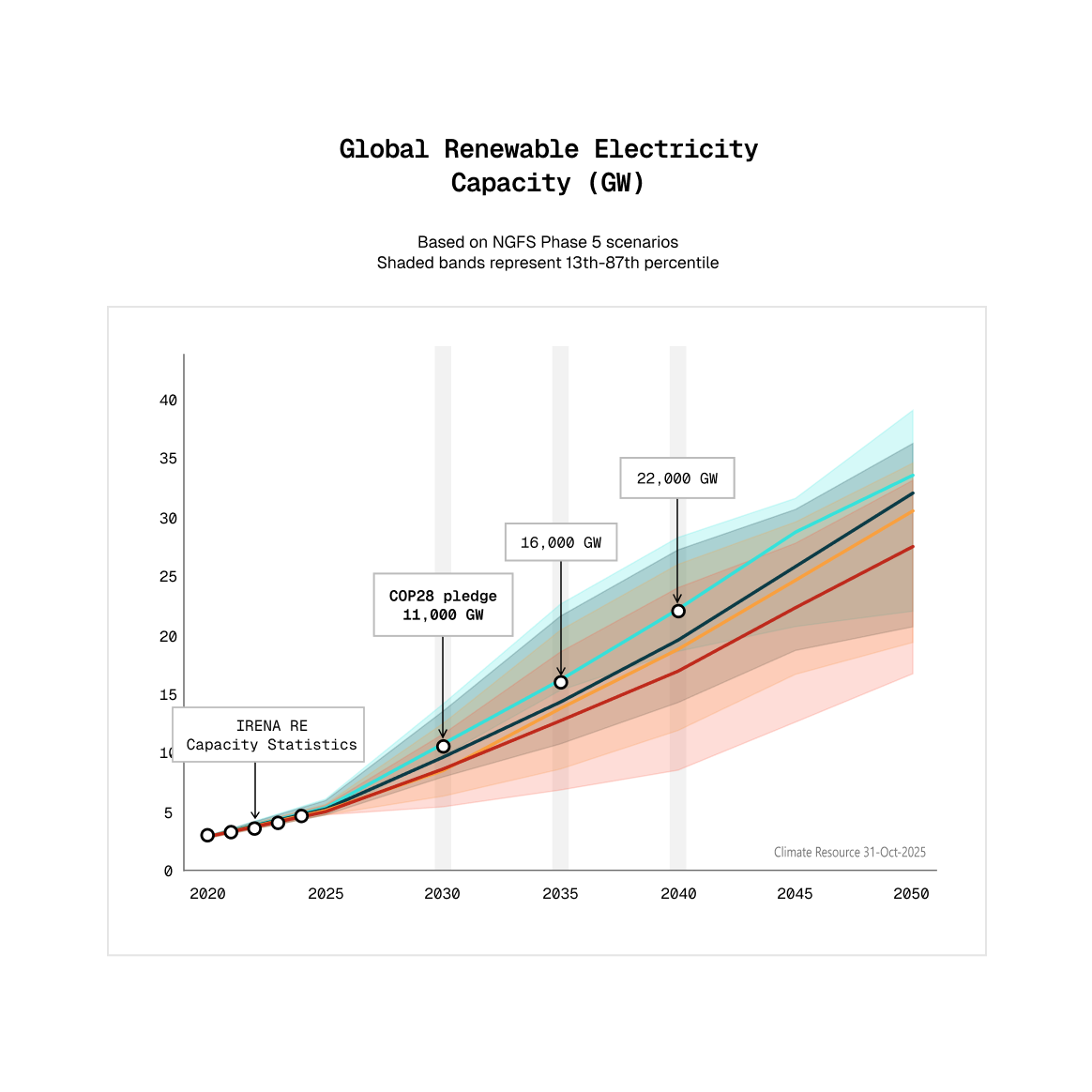
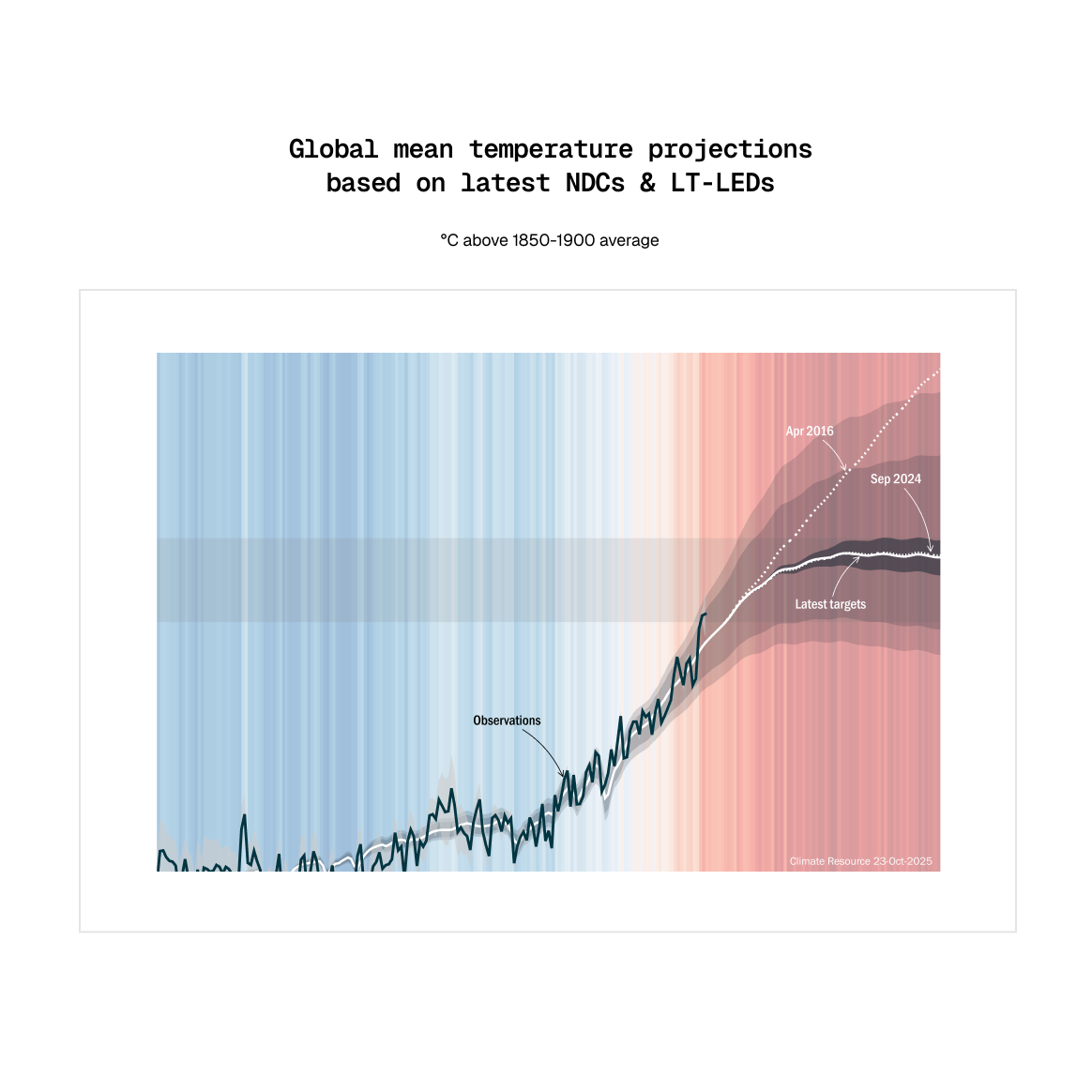
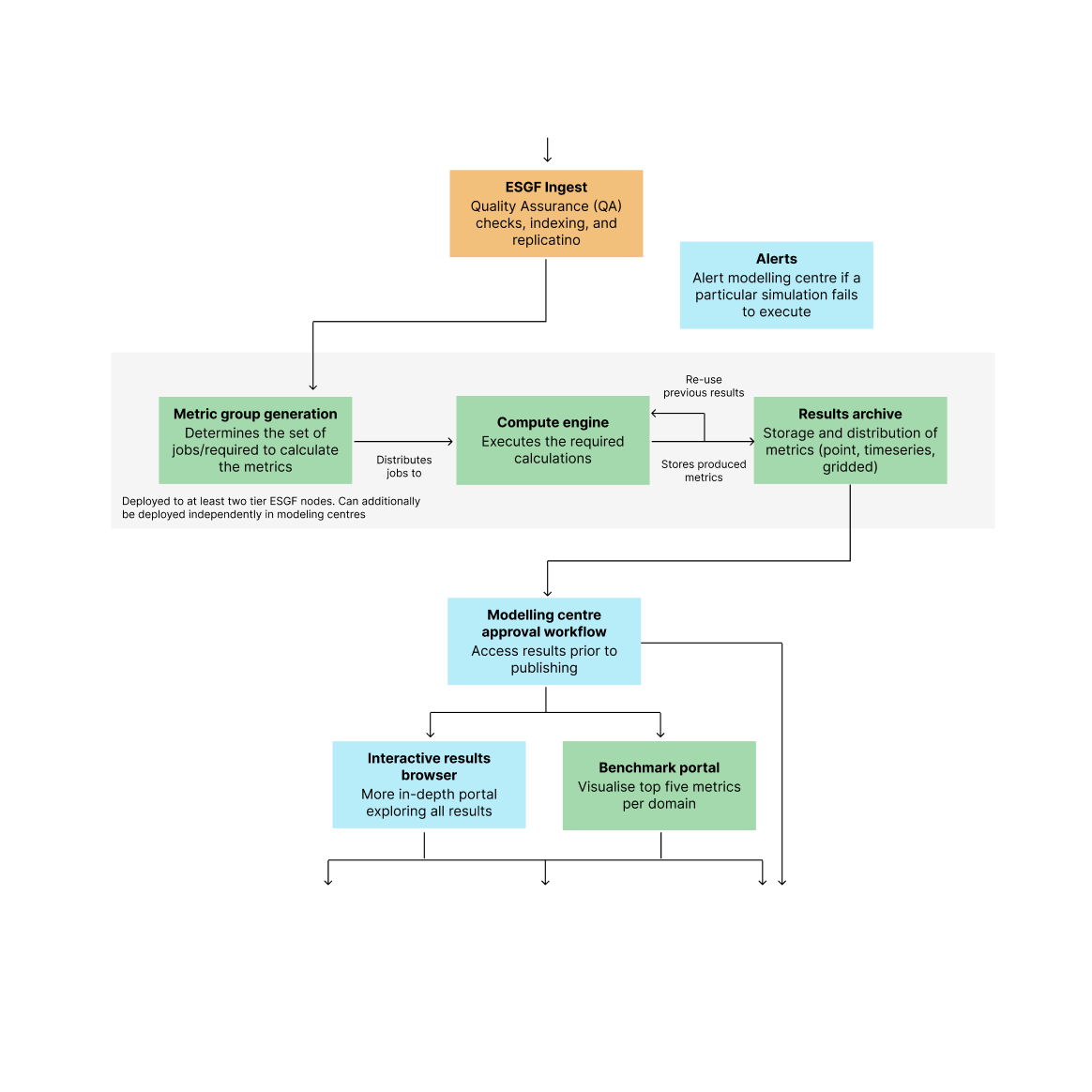
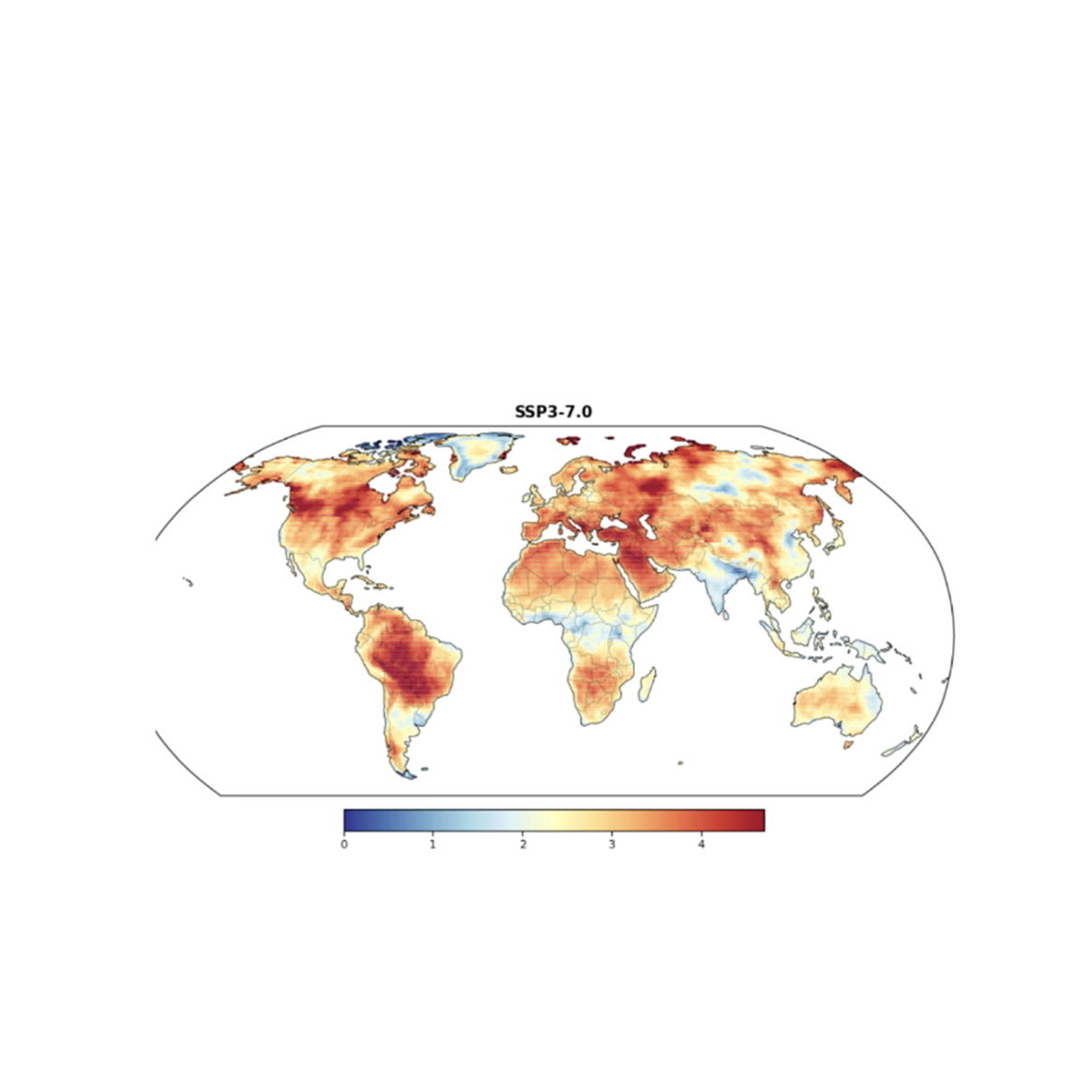
We help governments, multinational organisations, businesses, and communities understand risks and opportunities as the world decarbonises and responds to climate change.
Our models and data are widely used by the global science community and IPCC processes. We use these to provide clear, trustworthy insights - supporting action on climate change from the global stage to the local level.